

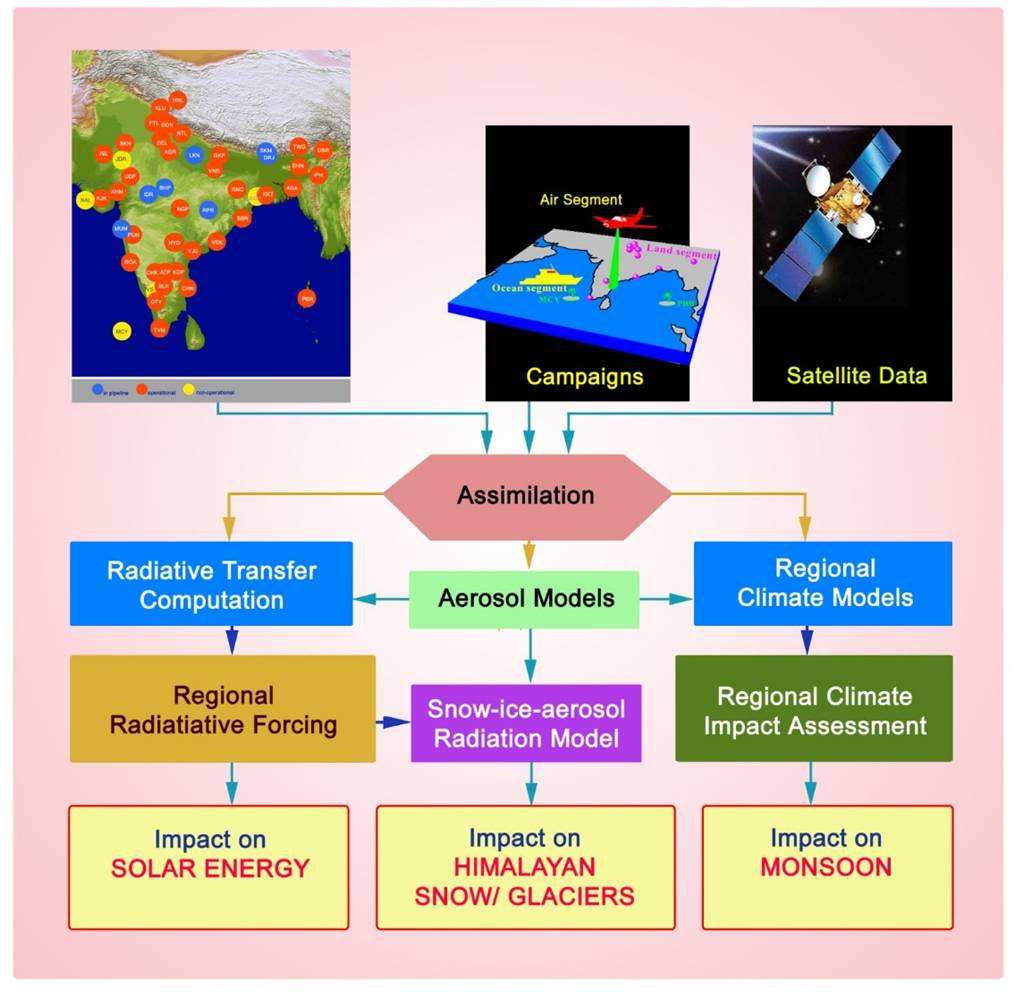
Climate impact of aerosols remains uncertain despite concentrated efforts of global scientific community. This is mainly because (a) aerosols are not represented in climate models with adequate spatio-temporal heterogeneity and (b) the climate models are not matured enough to faithfully represent aerosol impacts on regional/global scale. This calls for more accurate and resolved (space, time and spectral) assessments of physico-chemical properties of aerosols and better representation in models. Being a multi-parameter problem and owing to the large heterogeneity in space and time, isolated measurements are not adequate for accurate aerosol characterization; rather, the need is a sustained, region-specific, and synergistic approach. This is more so for India, with its large natural diversity, tropical nature, wide range of human activities, long coastline, vast semi-arid and arid regions and the contrasting monsoons.
The ARFI network is designed to make comprehensive measurements of all the aerosol parameters needed for climate impact assessment. In addition to the network stations, concerted (multi-disciplinary) campaign mode efforts (e.g., ICARB and RAWEX) involving concurrent measurements from diverse platforms onboard ships, high altitude balloons and aircrafts also form integral part of ARFI. This is supplemented with the measurements at background sites such as Antarctic, Arctic and Himalayas and satellite data complementing the network and campaign measurements, providing a synergy. Keeping the data from the network stations and campaigns as ground truths and anchoring points, the satellite retrieved parameters are compared, validated and used to fill the spatio-temporal gaps in the data sets. The ARFI database will be assimilated with the regional climate models for the assessment of climate impact of aerosols over India and the adjoining Oceans.
Aerosol Radiative Forcing over India (ARFI), Integrated Campaign for Aerosols, gases and Radiation Budget (ICARB) & Regional Aerosol Warming EXperiment (RAWEX) hold the three facets of the Aerosols and Cliate Forcing projects of SPL, being implemented under the ISRO-GBP.
Development of a primary aerosol database over the Indian subcontinent and adjoining oceans by establishing and operating a network of aerosol observatories and conducting thematic field campaigns
Estimation of regional aerosol radiative forcing using ARFINET database
Assimilation of ARFINET database with regional climate models for the assessment of potential climate impacts
Quantification of the climate implications of the elevated atmospheric warming by absorbing aerosols
Implications of long-term trend in aerosol loading on regional climate over Indian region
Assessment of the effect of absorbing aerosols through aerosol-cryosphere-atmosphere interactions
Investigations on Aerosol-Cloud interaction and indirect radiative forcing of aerosols
To understand the processes of new particle formation in different environments
Development of satellite payloads for accurate estimation of aerosol properties from space